Crafting cross-platform mobile applications becomes effortless with the right app development framework. However, there are important considerations to bear in mind.
While an optimal app development framework certainly streamlines the process, complexities persist, which we’ll delve into later in this blog.
In today’s rapidly evolving mobile app development landscape, businesses can’t afford to overlook their presence on both the Google Play Store and the Apple App Store. Moreover, budget constraints often hinder the adoption of native apps.
This is precisely why cross-platform app development has emerged as the unparalleled choice for businesses seeking a foothold on both Android and iOS platforms.
Before we explore where the cross-platform app development framework stands in 2025, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals.
What is Cross-Platform App Development?
As mobile apps assume an indispensable role in businesses, it’s crucial to comprehend the intricacies of app development. Cross-platform mobile development involves creating software applications that function across multiple mobile operating systems.
With cross-platform apps, developers can share a portion or even the entirety of the source code. This means that they can build and deploy mobile assets that operate on Android and iOS without duplicating efforts for each platform.
Why is it Important in 2025?
Cross-platform mobile app development enables developers to create applications using a single codebase, leading to reduced development costs. It also facilitates reaching a wider audience for your app. By providing a consistent user experience across different platforms, cross-platform mobile app development simplifies maintenance and updates.
Difference between Native and Cross-Platform App Development
The native versus cross-platform debate has long divided the tech community. Both native and cross-platform development technologies continue to evolve. This dynamic nature underscores the importance of periodically reevaluating these options to determine which ones are currently at the forefront. Native app development bypasses the complexities of creating a sustainable product that spans multiple platforms and instead focuses on delivering a cohesive design closely aligned with the target platform (e.g., Android, iOS, etc.).
Cross-platform frameworks aim to create an app that appeals to a broad base of followers by covering a range of devices during the programming and creation process.
Challenges Encountered in the Process of Developing Apps for Multiple Platforms
In the past, the scope of cross-platform app development was limited to creating basic mobile applications and games. However, advancements in technology have made cross-platform development more versatile, robust, and flexible.

1- Addressing Compatibility Issues with Different Operating Systems and Devices
One of the main challenges in cross-platform mobile app development is ensuring compatibility across various devices and operating systems. Problems may arise when apps are not designed to properly support the devices on which they are running, resulting in performance issues.
2- Limited Access to Device Hardware Features
Cross-platform frameworks operate differently on different devices, making it challenging to leverage the unique features of each device. This is primarily due to the lack of direct access to the hardware of these devices by the development tools.
3- Performance Issues Compared to Native Apps
Performance can be hindered by inconsistent communication between native and non-native components of devices, causing disruptions and affecting user experience.
4- Difficulty in Keeping Up with Operating System and Device Updates
Maintaining cross-compatibility of apps across various devices and operating systems poses a challenge for cross-platform app developers. It can be demanding to keep pace with the frequent updates released for different platforms.
Additional Challenges Faced in Cross-Platform Development Include:
- Maintaining cross-compliance of apps across devices and operating systems can be challenging for developers.
- Performance-related glitches can result in a subpar user experience.
- If a business app is responsible for managing a part of a company and storing user data, opting for cross-platform apps may not always be ideal due to security concerns.
Nevertheless, these challenges are outweighed by the advantages offered by cross-platform app development.
Benefits of Cross-Platform App Development
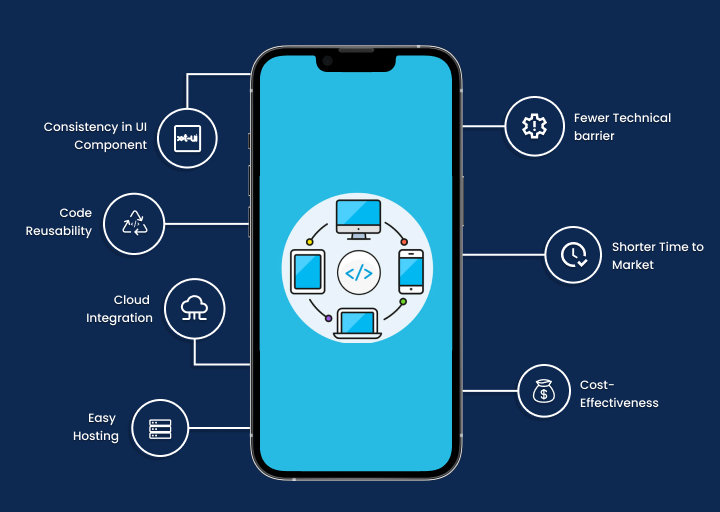
1- Maximizing Reach to the Target Audience
By adopting a mobile cross-platform development approach, companies can create and deploy apps across multiple platforms, including the web. With a single app targeting both iOS and Android platforms, the reach to the target audience is maximized.
2- Cost Reduction in Development
Cross-platform app development follows the principle of “write once, run everywhere.” Through reusable code and Agile app development processes and tools, development costs can be minimized. Cross-platform apps offer a cost-effective solution for businesses seeking to improve their presence on multiple platforms.
3- Simplified Maintenance and Deployment
In cross-platform app development, a universal app is compatible with all platforms, making maintenance and deployment easier. Code changes can be promptly synchronized across all platforms and devices, saving time and money. Additionally, if a bug is found in the common codebase, it only needs to be fixed once, leading to significant time and cost savings for developers.
4- Accelerated Development Process
Developing cross-platform apps leads to a faster development process. By utilizing a single source code for multiple platforms, development efforts can be reduced by 50 to 80%. This streamlined approach enables the creation of feature-rich business apps in less time, ensuring that development teams meet project deadlines.
5- Code Reusability
Cross-platform development offers the advantage of code reuse. Instead of creating new code for each platform, developers can reuse a single codebase. This saves time and resources by eliminating repetitive code creation tasks.
6- Seamless Cloud Integration
Cross-platform mobile apps are compatible with various cloud-integrated plug-ins. This means that a single source code can be coordinated with multiple plug-ins and extensions to enhance scalability and functionality.
7- Faster Time-to-Market and Customization
Adhering to the “write once, run everywhere” approach in cross-platform app development enables faster Time-to-Market (TTM) through quick deployment. If the app requires transformation or customization, developers can easily make minor changes in a single codebase. This agility allows for swift product delivery, enhancing customer engagement and outpacing competitors.
8- Consistent Design
Users can recognize and anticipate the user interface (UI) elements across different platforms. Therefore, maintaining a consistent User Experience (UX) is crucial for any app or software.
Synchronizing multiple development projects for individual apps can be challenging. Cross-platform mobile development tools empower developers and designers to create a unified user experience that app users can enjoy.
Open-source cross-platform app development frameworks based on programming languages
Top Cross-Platform App Development Frameworks
In the world of app development, there are numerous frameworks available for creating cross-platform applications. Each framework comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Below, we outline the leading frameworks that are currently dominating the market:
1- Xamarin
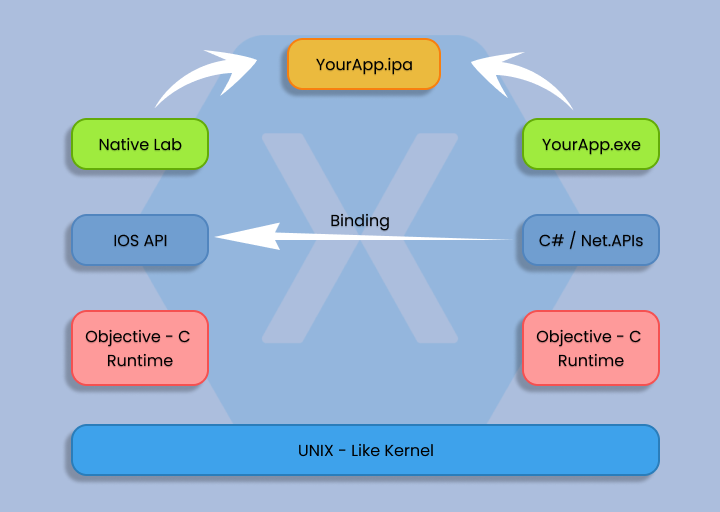
Xamarin, initially established as an independent cross-app development framework in 2011, gained increased credibility after being acquired by Microsoft in 2016. This open-source framework was designed to address the challenges posed by fragmented native technology stacks, which made mobile app development complex and costly.
Pros of Xamarin
- Cross-platform compatibility: Xamarin employs C# for coding, enabling seamless operation on various platforms, including Android and iOS.
- Vibrant community: With a robust community consisting of over 60,000 contributors from more than 3,700 companies, Xamarin benefits from active support and collaboration.
- Code sharing efficiency: Xamarin facilitates the sharing of over 75% of code across platforms, promoting the concept of “write once, run anywhere.”
Cons of Xamarin
- Enterprise cost: While Xamarin is free for individuals and startups, enterprises are required to purchase a license for Microsoft’s Visual Studio, making it expensive for larger organizations.
- Limitations in graphics-intensive apps: Xamarin is not recommended for applications that heavily rely on graphics, as each platform has its own visual layout method. It is advised to implement UX/UI-rich applications natively.
- Library restrictions: Xamarin provides limited access to crucial libraries necessary for mobile app development. Additionally, the process of creating user interfaces (UI) can be time-consuming due to the non-mobile nature of its UI creation core.
Apps made with Xamarin cross-platform app framework
- Fox Sports
- Alaska Airlines
- HCL
- American Cancer Society
- BBC Good Food
2- React Native
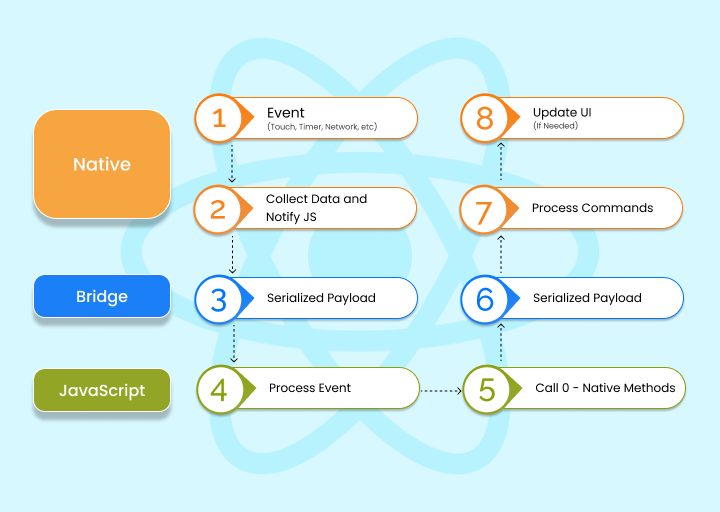
React Native, introduced by Facebook in 2015, made a significant impact on the market for hybrid frameworks. In just a few years, React Native has emerged as one of the most popular cross-platform app frameworks, surpassing the other four frameworks discussed in this blog.
Advantages of React Native
- Code reusability allows for sharing up to 80% of the codebase across platforms, resulting in faster development.
- React Native offers instant result previews and provides a wide range of ready-to-use elements, reducing development time significantly.
- The Hot Reloading feature enables developers to see code changes in seconds, enhancing productivity compared to native technologies.
- React Native focuses heavily on user interface (UI), resulting in highly responsive interfaces.
- It provides access to essential native functionalities such as the accelerometer and camera, enabling the creation of high-quality, native-like user interfaces.
Disadvantages of React Native
- React Native is not a fully cross-platform app framework, as certain functions like the camera or accelerometer still require the use of native components, resulting in separate code for Android and iOS. • Due to its independent development from iOS and Android, React Native occasionally lags behind native platforms. This was one of the reasons Udacity discontinued investing in React Native for new features.
• React Native lacks consistency in releasing updates.
• While React Native speeds up development, it can prolong the debugging process, particularly on Android.
Apps made with React native cross-platform app framework
- Bloomberg
- Skype
- Tesla
3- Flutter
Flutter, a free and open-source framework, allows developers to create native interfaces for both Android and iOS platforms. This blog explores the reasons behind its inclusion in the list of popular cross-platform tools and its enduring popularity.

Pros of Flutter:
- Rapid Code Changes: Flutter’s “Hot reloading” feature enables developers to see code modifications in seconds, providing a significant advantage over the traditional minutes-long waiting time.
- Ideal for MVP Development: Flutter serves as an excellent framework for Minimum Viable Product (MVP) development. Rather than investing additional time and money in separate Android and iOS apps, developers can quickly build a Flutter mobile application that appears native on both platforms.
- Easy to Learn: Built on Dart, an object-oriented programming language, Flutter is known for its relatively easy learning curve. Developers find it accessible to acquire the necessary skills.
- Extensive Widget Libraries: Flutter offers a comprehensive set of widgets, including Google’s Material Design and Apple’s Cupertino pack. These libraries facilitate the creation of visually appealing and intuitive user interfaces.
- Integration with Continuous Integration Platforms: Developers can seamlessly work with Continuous Integration platforms like Travis and Jenkins using many readily available solutions for native Android and iOS apps.
Cons of Flutter:
- Limited TV Support: Flutter’s framework lacks support for Android TV and Apple TV, limiting its applicability for developing apps on television platforms.
- Shortcomings Compared to Native Development: Despite being developed by Google and offering several ready-to-implement functionalities through libraries, Flutter still falls short in comparison to native development in certain areas.
- Larger App Size: Since Flutter apps utilize built-in widgets instead of platform widgets, the resulting app size tends to be larger. Currently, the smallest Flutter app weighs no less than 4MB.
By examining the advantages and disadvantages of Flutter, developers can make informed decisions when choosing a cross-platform framework for their app development projects.
Apps made with Flutter cross-platform app framework
- Alibaba
- Google Ads
- Tencent
Choosing the Best Cross-Platform App Development Framework for Your Project
Considerations for Selecting a Framework
- Empower Your Development Team: Ensure that your team is familiar with the tools and requirements of the chosen framework to save time and ease the learning process.
- Factors to Weigh: Take into account UX, total development time, budget, and maintenance requirements.
Comparing Frameworks Based on Different Criteria
- Audience Alignment: Check which supported frameworks align better with your target audience.
- Team Expertise: Evaluate the available expertise of your development team.
- Code Reusability: Assess the framework’s capability to reuse code across multiple platforms.
- Community Support: Look for community forums, documentation, and third-party libraries.
Tips and Best Practices for Cross-Platform App Development
- Maintain Visual Consistency: Utilize a set design system or UI library to ensure a cohesive user experience.
- Optimize Performance: Address potential performance issues caused by the abstraction layer by optimizing your code.
- Quick Tips: Employ caching and minimize network requests.
- Write Clean Code: Emphasize clarity, readability, and maintainability.
- Test Thoroughly: Conduct testing on multiple devices and platforms.
- Monitor User Experience: Continuously gather feedback and observe differences in user experience across different platforms.
Future of Cross-Platform App Development
As technology advances, the future of cross-platform app development is shaped by the following trends and emerging technologies:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Leverage AI tools for app testing, personalization, and optimization.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Integrate IoT to enhance user experience and connect with various devices.
- Low-Code and No-Code Platforms: Utilize these platforms to expedite development with minimal coding requirements.
- Cloud Technologies: Leverage cloud-based development for scalability, security, and easier maintenance.
Predictions for the Future of Cross-Platform App Development
- Increased Adoption: Cross-platform app development will be widely adopted due to its cost-effectiveness and efficiency.
- Enhanced Functionality: As technology improves, developers can create cross-platform apps with more advanced features.
- Improved User Experience: Integration of AI and IoT will lead to a seamless and personalized user experience.
- More Tools and Platforms: With growing demand, new tools and platforms will emerge, providing developers with more options and flexibility.
The Popularity of Cross-Platform Apps
Cross-platform apps eliminate the need to develop separate apps for different platforms, running seamlessly across devices. To create such universally compatible apps, a cross-platform framework is crucial. The choice of framework depends on the business and app’s functional requirements. Consulting an experienced cross-platform mobile app development company can help make an informed decision. Gather all the necessary information about app development frameworks before building a mobile app development solution for your customers.